Moody’s changes outlook for Vietnam’s banking system to negative on Covid-19
Prospects of foreign investment will dim in 2020, given the impact of the coronavirus outbreak on investment sentiment globally, and this will make it more difficult for Vietnamese banks to raise external capital.
Moody’s Investors Service has changed its outlook on 12 Asia Pacific banking systems, Vietnam’s included, to negative in light of the coronavirus outbreak and broad economic deterioration.
| The State Bank of Vietnam's headquarters in Hanoi. Photo: Minh Tuan |
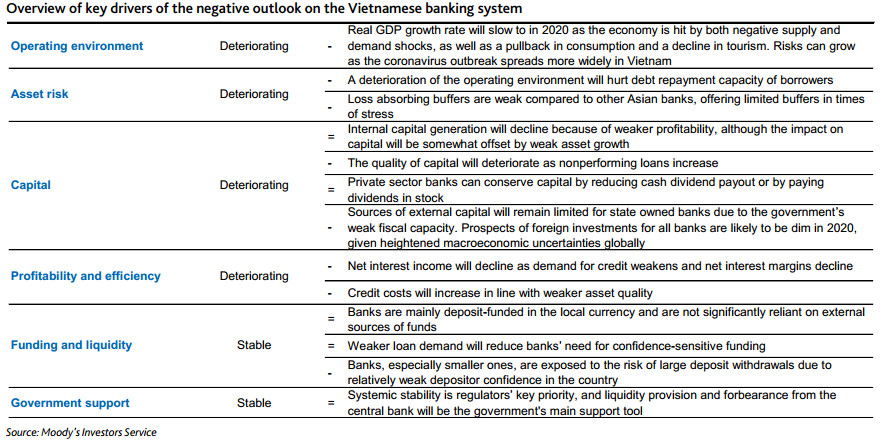
For Vietnam’s banking system, the change in outlook from stable reflects the impact of disruptions from the coronavirus outbreak on individuals and companies across different industries.
The US-based credit rating reckoned that Vietnam’s economy will face unprecedented challenges stemming from the coronavirus outbreak and macroeconomic challenges will renew asset stress. Debt repayment capacity of borrowers will deteriorate because of declines in revenue. A prolonged virus outbreak would lead to material increases in non-performing loans (NPLs) across multiple sectors, particularly the manufacturing and trade sectors, given Vietnam's large exposure and close ties to global supply chains.
In addition, contraction of net interest margins (NIMs) and increases in credit costs will weigh on profitability. The relief measures for borrowers, coupled with waning credit demand, will depress NIMs, while a deterioration in asset quality will lead to increases in loan loss provisions.
Capital quality will deteriorate because of increases in NPLs. While headline capital ratios will be stable as moderation of asset growth offsets declines in profit, the quality of capital will deteriorate as NPLs increase. Private sector banks can conserve capital by reducing cash dividend payouts or by paying dividends in stock. These options, however, could be less viable for state-owned banks that have historically paid high dividends.
Prospects of foreign investment will dim in 2020, given the impact of the coronavirus outbreak on investment sentiment globally, and this will make it more difficult for Vietnamese banks to raise external capital, according to Moody’s.
The rating firm said the Vietnamese government will support banks when needed despite limited capacity. The government will continue to provide support for banks, if needed, mainly in the form of liquidity assistance and regulatory forbearance from the central bank, as it has in the past.