Hanoi power consumption hits record high
Extreme weather conditions have sharply driven up electricity demand in the North, with Hanoi experiencing the most notable surge.
THE HANOI TIMES — Hanoi’s electricity consumption surged to a new record of 5,988 MW at 1:20 p.m. on August 4, marking a nearly 14% increase over the previous peak recorded in 2024, data from the Hanoi Power Corporation (EVNHANOI) revealed.
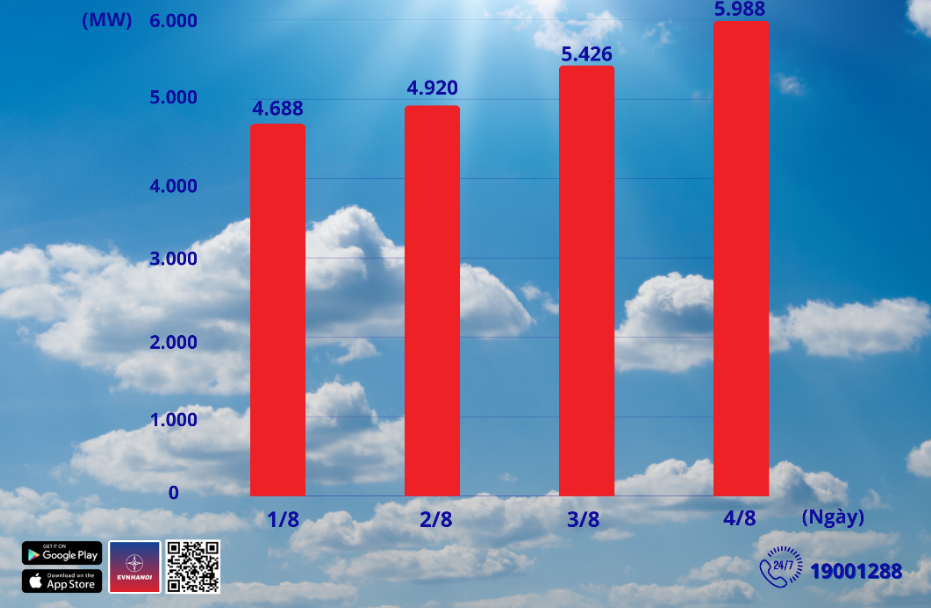
Electricity consumption in the capital over the past few days.Source: EVNHANOI
This sharp increase reflects a surge in electricity demand driven by prolonged hot weather, particularly among households using air conditioners and electric fans, noted the EVNHANOI.
Outdoor temperatures consistently ranging from 37 to 39°C have forced appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and electric fans to operate longer and work harder to maintain performance. As a result, electricity consumption has risen significantly, even when usage time remains unchanged.
The National Power System and Market Operator Company Limited (NSMO) yesterday [August 4] reported that following a heatwave at the end of July, Northern Vietnam has entered a new period of intense heat starting August 1. In Hanoi, temperatures approached 40°C on the same day, with readings at Lang Station ranging from 39.1°C to 39.7°C and a perceived temperature reaching 47°C, making it one of the hottest locations nationwide.
The extreme weather has significantly increased electricity demand in the North, including during weekends. Between August 1 and 4, peak electricity consumption in the region reached 25,761 MW, about 25% higher than on a typical weekend and nearly double the capacity of the Son La Hydropower Plant.

EVNHANOI workers on 24/7 duty to ensure power supply during heatwave days. Source: EVNHANOI
Nationally, power consumption peaked between 1:30 p.m. and 2:30 p.m. on August 4, reaching approximately 54,500 MW, the highest level so far this year and setting a new record. This figure is 5,000 MW, or 10%, higher than the same period in 2024. In the North alone, demand rose to 28,500 MW, up 3,000 MW (12%) year-on-year.
The surge in demand overloaded several transmission lines and transformers at 220kV and 500kV stations, including the 500kV Son La – Viet Tri line, the 220kV Thanh Cong – Ha Dong line, and major substations such as Hoa Binh, Lai Chau, Viet Tri, Tay Hanoi, Pho Noi, Thuong Tin, Hiep Hoa, Dong Anh, Mai Dong, Chem, Thanh Cong, Bac Ninh 2, Dong Hoa, and Ha Dong.
At 1:46 p.m., a fault occurred on the 220kV Hoa Binh – Ha Dong line, prompting NSMO to implement load adjustments, cutting electricity in select areas to ease pressure on overloaded lines and transformers, and prevent widespread outages. By 3:00 p.m., all affected loads were restored.
Between 9:00 p.m. and 11:00 p.m. on August 4, high temperatures in the North continued to persist, with electricity demand potentially rising to between 29,000 and 29,500 MW—1,000 MW higher than the afternoon peak. This continued increase had posed further pressure on the northern power grid.
In response, NSMO mobilized all available power sources in the region and is implementing technical measures in coordination with Vietnam Electricity (EVN), regional power corporations, and transmission units to ensure stable and uninterrupted grid operations.
NSMO urges households, businesses, and public agencies to use electricity efficiently, especially during peak hours. Recommended actions include using energy-efficient appliances, turning off unnecessary devices, unplugging equipment when not in use, and avoiding the simultaneous operation of multiple high-power devices.












